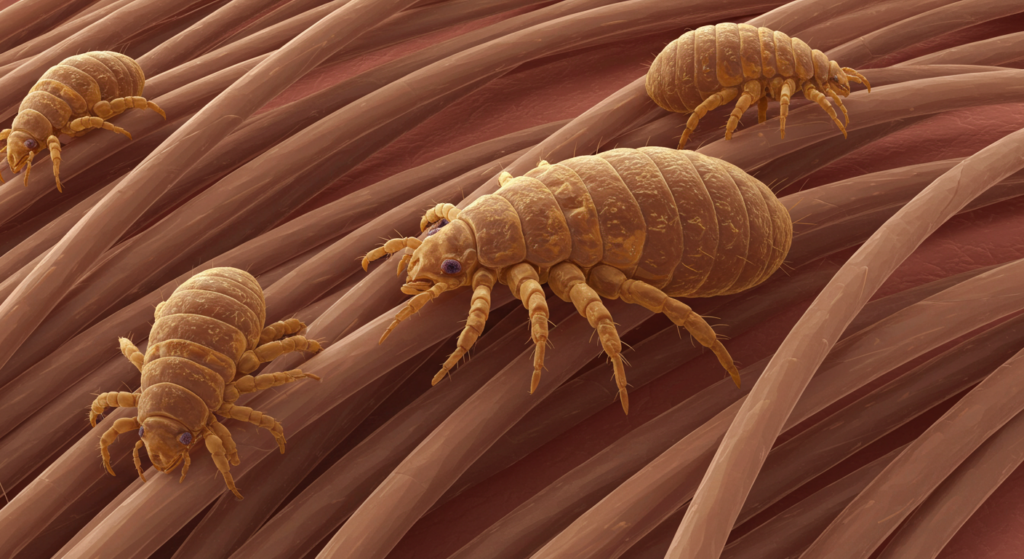
Las infestaciones de piojos, o pediculosis, son un problema común que afecta a millones de personas en todo el mundo. Estos diminutos insectos parásitos se alimentan de sangre humana, causando picazón, irritación y, en algunos casos, infecciones secundarias. Comprender los diferentes tipos de piojos (de la cabeza, del cuerpo y del pubis) y sus respectivos tratamientos es crucial para un manejo y una prevención eficaces. Este artículo ofrece una descripción general de cada tipo, destacando su identificación, las opciones de tratamiento y las estrategias preventivas.
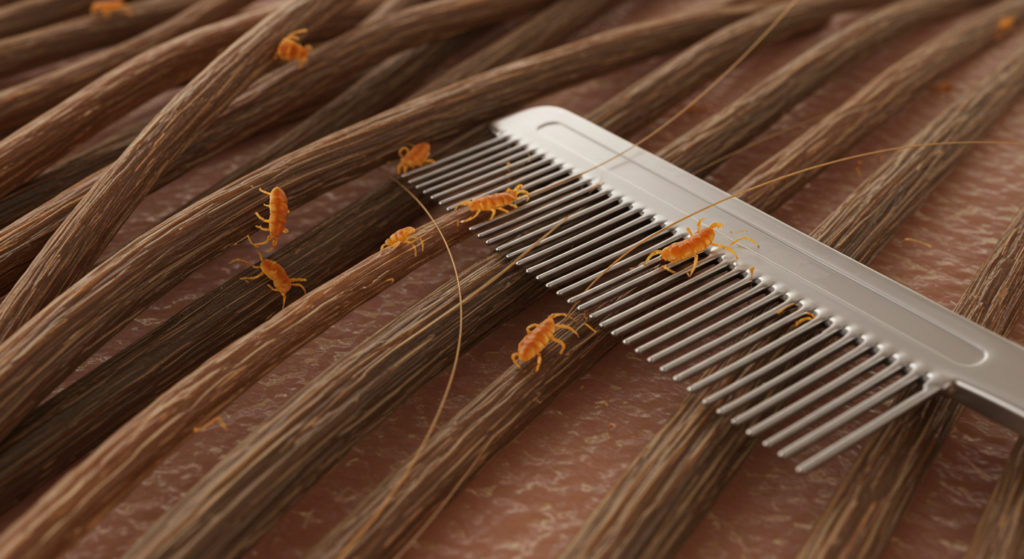
Piojos de la cabeza: identificación y tratamiento
Los piojos de la cabeza (Pediculus humanus capitis) son el tipo más común y afectan principalmente a los niños. Son pequeños insectos sin alas que viven y ponen sus huevos (liendres) en el cabello. Su identificación requiere un examen minucioso del cabello y el cuero cabelludo. Las liendres aparecen como diminutas motas blancas o grisáceas firmemente adheridas al tallo piloso, cerca del cuero cabelludo. Los piojos adultos son aproximadamente del tamaño de una semilla de sésamo y de color blanco grisáceo. Se mueven rápidamente, lo que a veces dificulta su detección. La picazón intensa es un síntoma característico, que a menudo provoca rascado y posibles infecciones cutáneas secundarias.
El tratamiento para los piojos de la cabeza suele consistir en el uso de pediculicidas de venta libre, medicamentos diseñados para eliminarlos. Estos productos suelen contener permetrina o piretrina, insecticidas naturales derivados de las flores de crisantemo. Es fundamental seguir las instrucciones del producto meticulosamente, ya que pueden ser necesarias varias aplicaciones para eliminar todos los piojos y liendres. Además de los tratamientos químicos, se recomienda encarecidamente la eliminación manual de las liendres con un peine de dientes finos. Este proceso requiere paciencia y persistencia, pero es esencial para prevenir la reinfestación. El peinado en húmedo, en el que se humedece bien el cabello con acondicionador antes de peinarlo, también puede ser eficaz.
Los tratamientos alternativos para los piojos incluyen remedios naturales como el aceite de árbol de té o el aceite de coco, aunque su eficacia está menos demostrada que la de los pediculicidas. Es importante consultar con un profesional de la salud si los remedios caseros resultan ineficaces o si se desarrollan infecciones cutáneas secundarias. Es posible que le recomienden medicamentos recetados más fuertes u otras estrategias de control. Las revisiones periódicas para detectar piojos y liendres, especialmente en niños, son esenciales para la detección temprana y el tratamiento oportuno.
La prevención implica revisarse la cabeza con regularidad, evitar el contacto directo con la cabeza y no compartir artículos personales como sombreros, peines y cepillos. Educar a los niños sobre la prevención de piojos y las prácticas de higiene también es crucial. Las escuelas y guarderías suelen implementar políticas para minimizar la propagación de piojos. El tratamiento oportuno y la prevención diligente son clave para controlar las infestaciones de piojos.
Piojos del cuerpo: Cómo reconocer y controlar las infestaciones
Los piojos del cuerpo (Pediculus humanus humanus) son similares en apariencia a los piojos de la cabeza, pero habitan en la ropa y la ropa de cama, en lugar del cabello. Se encuentran típicamente en las costuras de la ropa, especialmente en zonas cercanas al cuerpo. A diferencia de los piojos de la cabeza, las infestaciones de piojos del cuerpo suelen estar asociadas con la falta de higiene y el hacinamiento. Las picaduras de piojos del cuerpo causan picazón intensa, lo que lleva al rascado y a posibles infecciones bacterianas secundarias. Las picaduras suelen aparecer como pequeñas ronchas rojas, a veces dispuestas linealmente a lo largo del cuerpo.
El diagnóstico de infestaciones de piojos corporales implica un examen minucioso de la ropa y la ropa de cama. Los piojos adultos pueden ser visibles a simple vista, pero su pequeño tamaño puede dificultar su detección. La presencia de heces de piojos (pequeñas manchas oscuras) en la ropa es otro indicador de infestación. Es fundamental inspeccionar minuciosamente las costuras y los pliegues de la ropa, prestando especial atención a las zonas de contacto directo con el tejido. Un profesional de la salud puede confirmar el diagnóstico y recomendar el tratamiento adecuado.
El tratamiento para los piojos del cuerpo consiste en eliminarlos de la ropa y la ropa de cama. Esto suele implicar lavar toda la ropa y la ropa de cama con agua caliente (al menos a 54 °C) y secarla a alta temperatura. Las prendas que no se puedan lavar deben lavarse en seco o guardarse en bolsas de plástico selladas durante al menos dos semanas para eliminar los piojos y sus liendres. También se pueden usar pediculicidas de venta libre para tratar el cuerpo, pero es fundamental seguir atentamente las instrucciones del producto. Abordar las condiciones de higiene y de vida subyacentes es esencial para prevenir la reaparición.
Prevenir las infestaciones de piojos corporales requiere mantener una buena higiene, que incluye bañarse y lavar la ropa de cama y la ropa de cama con regularidad. También es importante evitar el contacto cercano con personas infestadas. En situaciones de hacinamiento o saneamiento deficiente, pueden ser necesarias intervenciones de salud pública para controlar la propagación de piojos corporales. Abordar los determinantes sociales subyacentes de la salud es crucial para prevenir y controlar las infestaciones de piojos corporales, especialmente en poblaciones vulnerables.
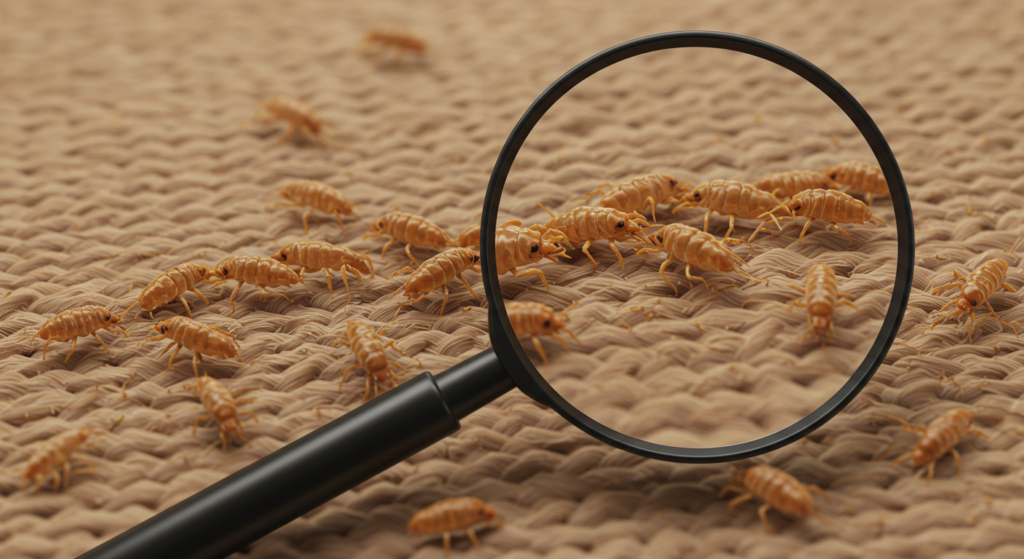

Piojos púbicos (ladillas): diagnóstico y erradicación
Los piojos púbicos (Pthirus pubis), también conocidos como ladillas, son una infección de transmisión sexual (ITS) que infesta principalmente el vello púbico. Son más grandes que los piojos de la cabeza o del cuerpo y tienen una apariencia similar a la de una ladilla. Se adhieren al vello púbico, se alimentan de sangre y causan una picazón intensa. Si bien el vello púbico es el sitio de infestación más común, a veces se encuentran en otras zonas con vello, como las axilas, las cejas o las pestañas. El diagnóstico suele realizarse mediante un examen visual de la zona afectada.
El tratamiento para las ladillas púbicas suele consistir en el uso de pediculicidas de venta libre, diseñados específicamente para ellas. Estos productos, al igual que los utilizados para la pediculosis de la cabeza, suelen contener permetrina o piretrina. Es fundamental seguir atentamente las instrucciones del producto y aplicar el medicamento cuidadosamente en todas las zonas afectadas. Al igual que en el tratamiento para la pediculosis de la cabeza, la extracción manual de las liendres con un peine de dientes finos puede ser útil. Rasurar la zona afectada también puede ser eficaz, ya que elimina los piojos y sus liendres.
Los tratamientos alternativos para los piojos púbicos incluyen remedios naturales como el aceite de árbol de té o el aceite de coco, pero su eficacia no está tan bien demostrada. En casos de infestaciones graves o si los tratamientos de venta libre no son eficaces, un profesional de la salud podría recomendar medicamentos recetados más fuertes. Es fundamental tratar a todas las parejas sexuales para prevenir la reinfestación. También se recomienda la abstinencia sexual hasta completar el tratamiento.
Prevenir las infestaciones de piojos púbicos implica practicar sexo seguro, incluyendo el uso de preservativos. También es importante evitar el contacto cercano con personas que puedan tener infestaciones. Revisar regularmente la zona púbica para detectar piojos y liendres ayuda a la detección temprana y al tratamiento oportuno. La comunicación abierta con las parejas sexuales es crucial para controlar y prevenir la propagación de los piojos púbicos.

Prevención de infestaciones de piojos: estrategias efectivas
La prevención de las infestaciones de piojos implica un enfoque multifacético centrado en la higiene, la educación y las medidas proactivas. Las revisiones periódicas de la cabeza, especialmente en niños, son cruciales para la detección temprana. Esto permite un tratamiento oportuno y minimiza el riesgo de propagación de la infestación. Los padres y cuidadores deben recibir capacitación para identificar piojos y liendres, comprendiendo su apariencia y ubicación en el cuero cabelludo o el cuerpo. La intervención temprana es clave para prevenir infestaciones generalizadas en familias o comunidades.
Evitar el contacto directo con la cabeza, especialmente en entornos concurridos como escuelas o guarderías, es una medida preventiva eficaz. Desaconsejar compartir artículos personales como sombreros, peines, cepillos para el pelo y auriculares también puede reducir significativamente el riesgo de transmisión. Estos artículos pueden albergar fácilmente piojos y liendres, lo que facilita la propagación de infestaciones. Lavar regularmente la ropa de cama, la ropa y las toallas con agua caliente es esencial para eliminar cualquier piojo o liendre que pueda estar presente.
Mantener una buena higiene personal, incluyendo bañarse y ducharse regularmente, puede ayudar a reducir la atracción del cuero cabelludo o del cuerpo a los piojos. Si bien la higiene por sí sola no previene las infestaciones por completo, contribuye a crear un entorno menos propicio para la proliferación de piojos. Educar a niños y adultos sobre la prevención de piojos y las prácticas adecuadas de higiene es crucial para mantener un entorno saludable y minimizar el riesgo de infestaciones. Promover la concienciación y la comprensión de la transmisión de piojos permitirá a las personas tomar medidas proactivas para protegerse.
En entornos como escuelas y guarderías, es fundamental implementar políticas y procedimientos claros para el manejo de las infestaciones de piojos. Estas políticas deben incluir directrices para identificar, tratar y prevenir la propagación de los piojos. La colaboración entre escuelas, padres y profesionales de la salud es crucial para el manejo y la prevención eficaces de las infestaciones de piojos en la comunidad. La comunicación y la educación regulares pueden garantizar que todos comprendan la importancia de las medidas proactivas para mantener un entorno saludable.
Las infestaciones de piojos son un problema común, pero tratable. Comprender los diferentes tipos de piojos, su identificación y las opciones de tratamiento adecuadas es crucial para un manejo y una prevención eficaces. Al implementar estrategias preventivas y buscar atención médica inmediata cuando sea necesario, las personas y las comunidades pueden minimizar el impacto de estas infestaciones parasitarias. Recuerde que la detección temprana y el cumplimiento constante de los planes de tratamiento son clave para la erradicación exitosa y la prevención de futuras incidencias.
Descubra la experiencia de la Dra. Ebru Okyay, su médico de confianza. dermatólogo en AntalyaYa sea que esté buscando abordar problemas médicos de la piel o mejorar su belleza natural con tratamientos cosméticos, el Dr. Okyay está aquí para ayudarlo. Con atención personalizada y técnicas avanzadas, lograr sus objetivos para la piel nunca ha sido tan fácil.
