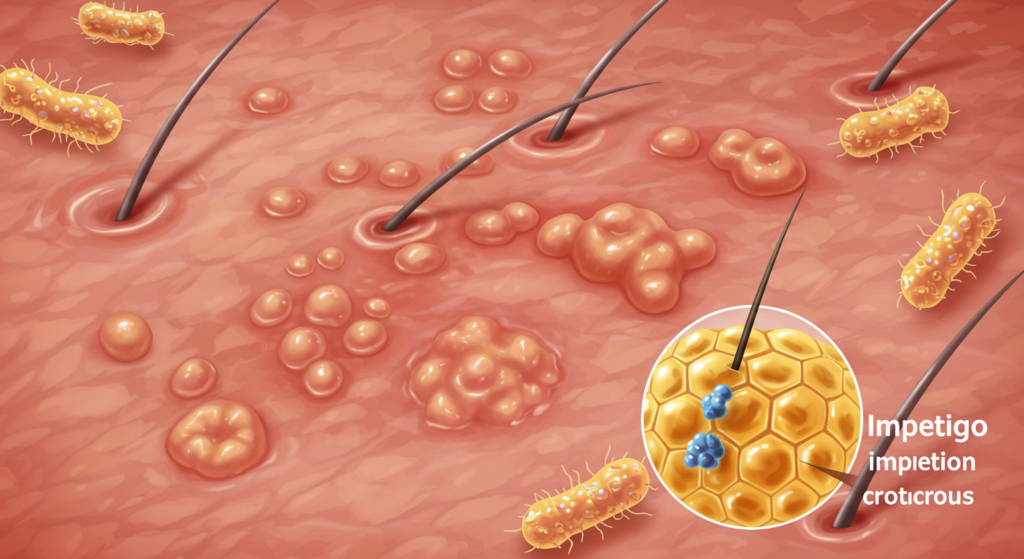
El impétigo es una infección bacteriana cutánea altamente contagiosa que afecta principalmente a bebés y niños. Se caracteriza por llagas y ampollas, por lo que es fundamental comprender sus síntomas, causas y métodos de tratamiento eficaces para prevenir su propagación y asegurar una pronta recuperación. Este artículo ofrece una visión general del impétigo, brindando a los lectores los conocimientos necesarios para reconocer, controlar y tratar esta afección cutánea común.
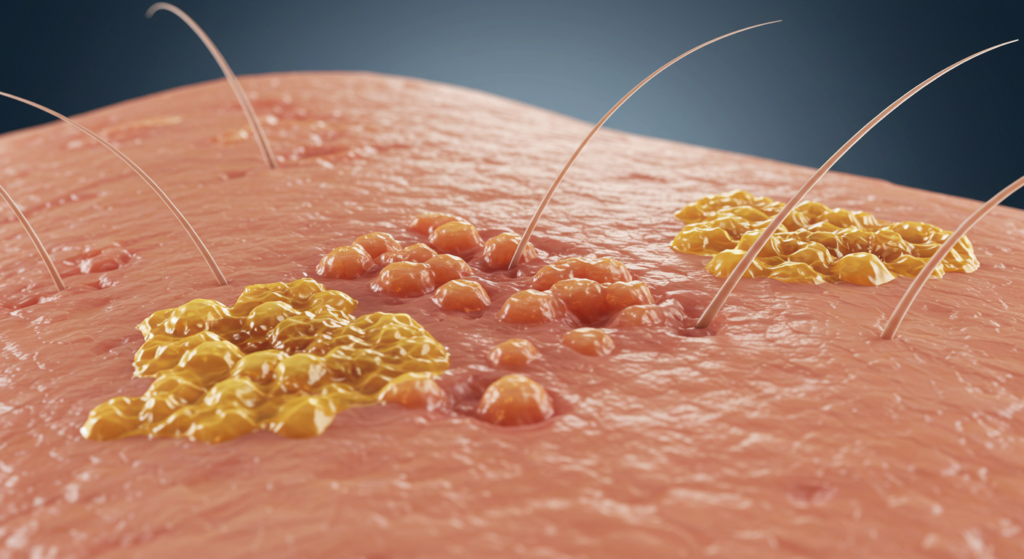
Comprensión del impétigo: una descripción general
El impétigo es una infección bacteriana superficial de la piel, comúnmente causada por las bacterias Staphylococcus aureus o Streptococcus pyogenes. Estas bacterias suelen penetrar en el cuerpo a través de pequeñas heridas en la piel, como cortes, raspaduras, picaduras de insectos o incluso eccemas. La infección es altamente contagiosa y se propaga fácilmente por contacto directo con personas infectadas u objetos contaminados. Si bien afecta principalmente a niños, los adultos también pueden contraer impétigo. La afección no suele ser grave, pero el tratamiento inmediato es esencial para prevenir complicaciones y la propagación de la infección. El impétigo sin tratamiento puede provocar infecciones cutáneas más graves o incluso extenderse a otras partes del cuerpo.
El impétigo se manifiesta en dos formas principales: no ampolloso y ampolloso. El impétigo no ampolloso comienza con pequeñas llagas rojas que se rompen rápidamente y forman costras de color miel. El impétigo ampolloso, por otro lado, se caracteriza por ampollas más grandes llenas de líquido que se abren y dejan costras similares de color miel. Ambas formas son altamente contagiosas y requieren atención médica adecuada. La ubicación de la infección puede variar, pero con frecuencia aparece en la cara, alrededor de la nariz y la boca, y en las extremidades. La gravedad de la infección también puede variar según el sistema inmunitario de la persona y el tipo de bacteria involucrada.
El diagnóstico de impétigo se realiza generalmente mediante un examen clínico realizado por un profesional de la salud. Una inspección visual de las llagas y ampollas características suele ser suficiente para el diagnóstico. En algunos casos, se puede tomar una muestra de hisopado de la zona afectada para identificar la bacteria específica causante de la infección y confirmar el diagnóstico. Esto permite un tratamiento específico y garantiza la aplicación del enfoque más eficaz. El diagnóstico y el tratamiento tempranos son cruciales para prevenir la propagación de la infección y minimizar las complicaciones.
Comprender la naturaleza contagiosa del impétigo es fundamental para una prevención y un tratamiento eficaces. Las buenas prácticas de higiene, como el lavado frecuente de manos y evitar el contacto cercano con personas infectadas, son esenciales. Mantener las heridas de la piel limpias y cubiertas también puede ayudar a prevenir la propagación de la infección. La atención médica inmediata es crucial para una pronta recuperación y para prevenir las posibles complicaciones asociadas con el impétigo no tratado.
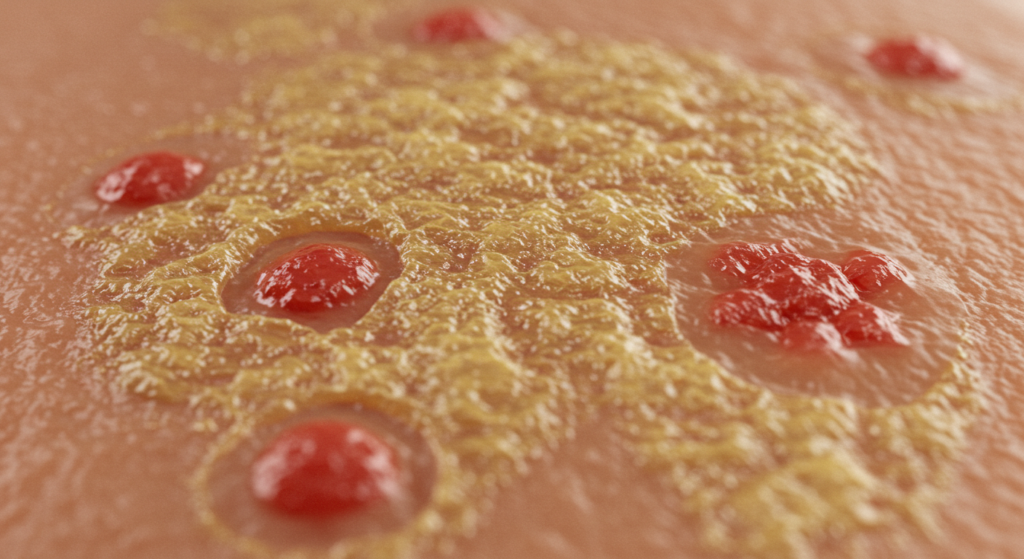
Reconociendo los síntomas clave del impétigo
El síntoma más característico del impétigo es la aparición de llagas o ampollas en la piel. En el impétigo no ampolloso, estas llagas comienzan como pequeñas protuberancias rojas que se abren rápidamente, dejando una costra característica de color miel. Estas costras pueden causar picazón y estar acompañadas de una leve molestia o dolor. Las llagas suelen aparecer en zonas expuestas de la piel, como la cara, alrededor de la nariz y la boca, y en las extremidades. Sin embargo, pueden aparecer en cualquier parte del cuerpo.
El impétigo ampolloso, en cambio, se presenta con ampollas más grandes, llenas de líquido, que suelen ser indoloras. Estas ampollas finalmente se rompen, liberando un líquido transparente que rápidamente se vuelve turbio y forma costras de color miel. Al igual que el impétigo no ampolloso, estas lesiones pueden causar picazón y molestias. La ubicación de estas ampollas también es variable, aunque se encuentran con frecuencia en la cara, el tronco y las extremidades.
Si bien las llagas y ampollas son los signos distintivos del impétigo, también pueden presentarse otros síntomas. Estos pueden incluir fiebre leve, inflamación de los ganglios linfáticos cerca de la zona afectada y malestar general. Sin embargo, estos síntomas adicionales no siempre están presentes, y el principal indicador de impétigo siguen siendo las llagas y ampollas características. Es importante tener en cuenta que la gravedad de los síntomas puede variar según la persona y la extensión de la infección.
Es fundamental distinguir el impétigo de otras afecciones cutáneas. Afecciones como el eccema, el herpes simple y las infecciones fúngicas pueden presentar síntomas similares. Por lo tanto, es fundamental obtener un diagnóstico preciso de un profesional de la salud para garantizar el tratamiento adecuado. El autotratamiento del impétigo puede retrasar la atención adecuada y potencialmente causar complicaciones. Si sospecha que tiene impétigo, consulte a un médico de inmediato para obtener un diagnóstico y tratamiento precisos.
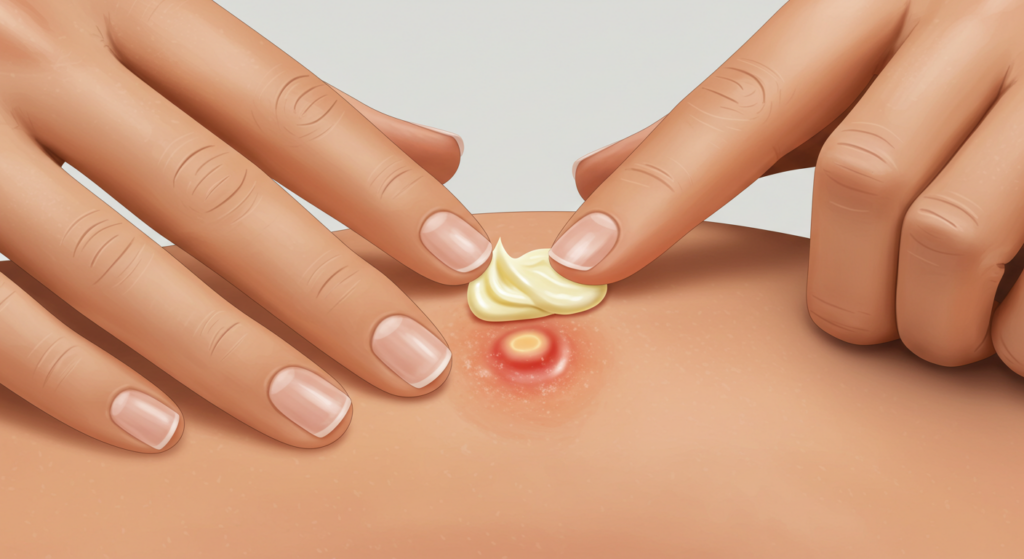
Descubriendo las causas del impétigo
El impétigo es causado principalmente por infecciones bacterianas, más comúnmente por Estafilococo áureo o Streptococcus pyogenesEstas bacterias se encuentran comúnmente en la piel y la nariz, y no suelen causar infección a menos que penetren a través de una ruptura de la barrera protectora de la piel. Lesiones menores como cortes, raspaduras, picaduras de insectos o incluso eccemas pueden crear aberturas por las que estas bacterias penetran e inician una infección. Las bacterias luego se multiplican, causando las llagas y ampollas características del impétigo.
La naturaleza contagiosa del impétigo implica que se propaga fácilmente por contacto directo con una persona infectada u objetos contaminados. Compartir toallas, ropa o ropa de cama con una persona infectada puede transmitir fácilmente la bacteria. Rascarse las zonas infectadas y luego tocar otras partes del cuerpo también puede propagar la infección. Además, las malas prácticas de higiene pueden contribuir a la propagación y persistencia de la bacteria, lo que aumenta la probabilidad de que se desarrolle una infección.
Ciertos factores pueden aumentar el riesgo de desarrollar impétigo. Las personas con sistemas inmunitarios debilitados son más susceptibles a las infecciones bacterianas, incluido el impétigo. Los niños, especialmente los que asisten a guarderías o escuelas, corren un mayor riesgo debido al contacto cercano con otros niños. Los climas cálidos y húmedos también pueden crear condiciones que favorecen el crecimiento y la propagación de bacterias, lo que aumenta la probabilidad de infección. Afecciones cutáneas subyacentes, como el eccema, también pueden aumentar la susceptibilidad al impétigo.
Comprender las causas del impétigo es crucial para una prevención eficaz. Mantener buenas prácticas de higiene, como lavarse las manos con frecuencia y evitar el contacto cercano con personas infectadas, es esencial. Mantener limpias y cubiertas las heridas menores de la piel puede ayudar a prevenir la entrada de bacterias. El tratamiento oportuno de las afecciones cutáneas existentes también puede reducir el riesgo de desarrollar impétigo.

Métodos eficaces de tratamiento del impétigo
El tratamiento del impétigo suele consistir en antibióticos tópicos u orales. Los antibióticos tópicos, aplicados directamente en la zona afectada, suelen ser la primera opción de tratamiento en casos leves. Estas cremas o ungüentos contienen antibióticos que eliminan eficazmente las bacterias causantes de la infección. Entre los antibióticos tópicos que se recetan habitualmente se encuentran la mupirocina (Bactroban) y el ácido fusídico. Estos suelen aplicarse varias veces al día durante varios días o semanas, según la gravedad de la infección y la respuesta del paciente al tratamiento.
En casos más graves de impétigo o cuando el tratamiento tópico resulta ineficaz, pueden ser necesarios antibióticos orales. Los antibióticos orales ofrecen un enfoque sistémico para combatir la infección, llegando a zonas donde los tratamientos tópicos no pueden penetrar eficazmente. Los antibióticos orales que se recetan habitualmente incluyen penicilina, amoxicilina y cefalexina. La elección del antibiótico y la duración del tratamiento dependerán de la gravedad de la infección y de las bacterias específicas implicadas. Es fundamental completar el tratamiento antibiótico completo, incluso si los síntomas mejoran antes de la fecha de finalización prescrita, para prevenir la recurrencia.
Además del tratamiento con antibióticos, las buenas prácticas de higiene son esenciales para controlar el impétigo. Lavarse las manos con regularidad ayuda a prevenir la propagación de la infección. Mantener la zona afectada limpia y seca también puede ayudar a promover la cicatrización. Remojar la zona afectada en agua tibia con un jabón suave puede ayudar a eliminar las costras y facilitar la aplicación de tratamientos tópicos. Evite rascarse la zona afectada para prevenir una mayor propagación de la infección y reducir el riesgo de cicatrices.
Aunque el impétigo suele resolverse con tratamiento antibiótico, es importante consultar a un médico para un diagnóstico y tratamiento adecuados. Un profesional de la salud puede evaluar la gravedad de la infección y determinar el tratamiento más adecuado. También puede supervisar la evolución del paciente y abordar cualquier complicación que pueda surgir. La intervención temprana y el tratamiento adecuado son cruciales para prevenir complicaciones y garantizar una pronta recuperación.
El impétigo, aunque es una infección cutánea común, requiere atención inmediata y un tratamiento adecuado. Comprender sus síntomas, causas y métodos de tratamiento eficaces es crucial para prevenir su propagación y asegurar una pronta recuperación. Mantener una buena higiene y consultar a un médico cuando sea necesario son clave para controlar esta enfermedad contagiosa eficazmente. Recuerde consultar siempre con un profesional de la salud para obtener diagnóstico y tratamiento.
Descubra la experiencia de la Dra. Ebru Okyay, su médico de confianza. dermatólogo en AntalyaYa sea que esté buscando abordar problemas médicos de la piel o mejorar su belleza natural con tratamientos cosméticos, el Dr. Okyay está aquí para ayudarlo. Con atención personalizada y técnicas avanzadas, lograr sus objetivos para la piel nunca ha sido tan fácil.