La urticaria, también conocida como ronchas, es una afección cutánea común que se caracteriza por ronchas o habones que pican y abultan. Estas ronchas pueden variar en tamaño y ubicación, apareciendo repentinamente y desapareciendo con la misma rapidez. Si bien no suele ser una afección médica grave, la urticaria puede ser muy incómoda y perturbar la vida diaria. Comprender las causas, los síntomas y las opciones de tratamiento es crucial para un manejo y alivio efectivos. Este artículo ofrece una descripción general completa de esta afección cutánea.
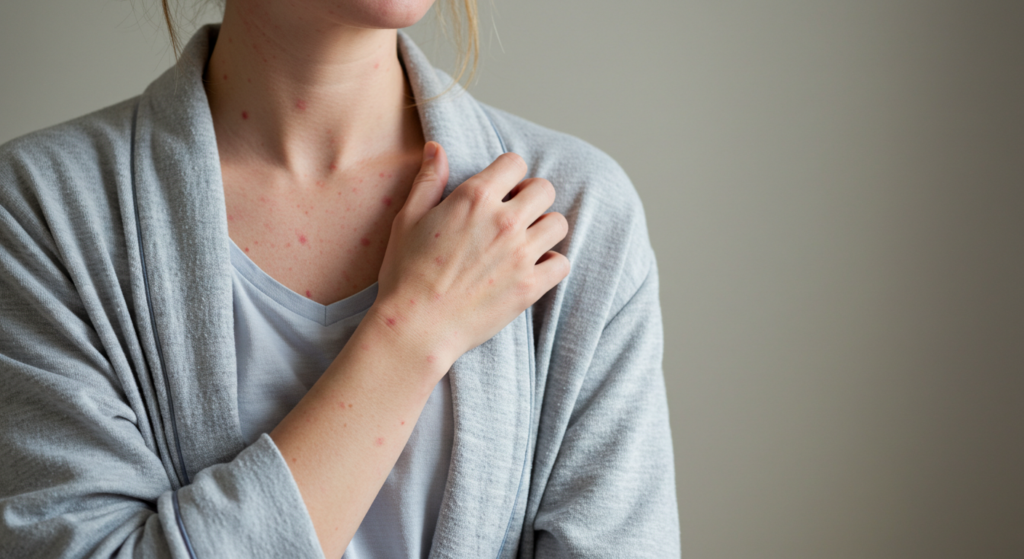

Entendiendo la urticaria: Una visión general completa
La urticaria es un tipo de reacción alérgica que afecta la piel. Las características ronchas elevadas se deben a la liberación de histamina y otras sustancias químicas inflamatorias de los mastocitos de la piel. Esta liberación aumenta el flujo sanguíneo a la zona afectada, lo que provoca la hinchazón y el enrojecimiento asociados a la urticaria. La aparición de la urticaria puede ser impredecible; puede aparecer en una zona y luego desaparecer, para luego reaparecer en otra.
La duración de cada urticaria puede variar de minutos a horas. Si bien la mayoría de los casos de urticaria son agudos y duran menos de seis semanas, algunas personas experimentan urticaria crónica, que persiste durante seis semanas o más. Comprender la causa subyacente de la urticaria es importante para determinar el mejor tratamiento.
La gravedad de la urticaria puede variar considerablemente. Algunas personas experimentan solo unas pocas ronchas pequeñas, mientras que otras pueden presentar urticaria extensa que cubre una parte significativa del cuerpo. En casos graves, la urticaria puede ir acompañada de angioedema, una inflamación más profunda que afecta los tejidos subcutáneos, a menudo en la cara, los labios y la garganta. El angioedema puede ser especialmente peligroso si afecta las vías respiratorias, causando dificultad para respirar. Por lo tanto, es fundamental buscar atención médica si experimenta síntomas de angioedema o si la urticaria se acompaña de otros síntomas preocupantes, como dificultad para respirar, mareos o desmayos.
La causa exacta de la urticaria no siempre es identificable. Sin embargo, muchos casos se desencadenan por una alergia subyacente u otra afección médica. Si bien algunas personas pueden experimentar urticaria como reacción a alérgenos específicos, como alimentos, medicamentos o picaduras de insectos, otras pueden desarrollarla debido a trastornos autoinmunes, infecciones o incluso estrés y estímulos físicos como el calor o el frío. La imprevisibilidad de la urticaria dificulta el diagnóstico y el tratamiento, lo que requiere una evaluación cuidadosa de los desencadenantes y síntomas individuales. Un diagnóstico preciso es fundamental para establecer un plan de tratamiento eficaz.
La urticaria crónica, que dura más de seis semanas, suele requerir una investigación más exhaustiva para identificar cualquier trastorno autoinmune subyacente u otras afecciones médicas que puedan contribuir a la roncha persistente. En estos casos, dermatólogo El alergólogo puede realizar pruebas adicionales, como análisis de sangre o pruebas cutáneas, para identificar posibles desencadenantes y orientar las decisiones de tratamiento. El tratamiento eficaz de la urticaria crónica suele implicar una combinación de medicamentos y cambios en el estilo de vida para minimizar los síntomas y mejorar la calidad de vida.
Causas comunes y desencadenantes de la urticaria
Las alergias alimentarias son una causa frecuente de urticaria, y entre los culpables más comunes se incluyen los frutos secos, el marisco, los huevos, la leche y el trigo. Incluso alimentos aparentemente inocuos pueden desencadenar una reacción en personas susceptibles. Los medicamentos, en particular ciertos antibióticos, analgésicos y medicamentos para la presión arterial, también pueden inducir urticaria como reacción adversa. Las picaduras de insectos, como abejas, avispas, hormigas y mosquitos, son otro desencadenante común, ya que liberan sustancias que pueden causar una respuesta alérgica inmediata. En algunos casos, el contacto con ciertas sustancias, como plantas (como la hiedra venenosa) o productos químicos, puede provocar urticaria localizada en el punto de contacto.
Las infecciones, tanto víricas como bacterianas, también pueden desencadenar urticaria como parte de la respuesta inmunitaria del cuerpo. Afecciones como resfriados, gripe y faringitis estreptocócica pueden estar asociadas con el desarrollo de urticaria. Las enfermedades autoinmunes, en las que el sistema inmunitario ataca por error a sus propios tejidos, pueden contribuir a la urticaria crónica. Algunos ejemplos son los trastornos tiroideos autoinmunes y el lupus. Los estímulos físicos, como el calor, el frío, la presión, la luz solar o las vibraciones, también pueden actuar como desencadenantes en algunas personas. Estas urticarias físicas se caracterizan por la aparición de urticaria en respuesta a estímulos físicos específicos.
El estrés emocional y la ansiedad pueden desempeñar un papel importante en el desencadenamiento o la exacerbación de la urticaria. La respuesta del cuerpo al estrés puede liberar sustancias químicas que promueven la inflamación, lo que lleva al desarrollo de la urticaria. Los cambios hormonales, especialmente en las mujeres, también pueden influir en la aparición de la urticaria, ya que las fluctuaciones en los niveles hormonales durante la menstruación o el embarazo a veces desencadenan o empeoran los síntomas. Finalmente, ciertas afecciones médicas subyacentes, como enfermedades autoinmunes, trastornos tiroideos e incluso algunos tipos de cáncer, pueden estar asociadas con la urticaria crónica.
Identificar el desencadenante específico de la urticaria puede ser difícil, y no siempre es posible. Llevar un registro detallado de los posibles desencadenantes, síntomas y el momento en que aparecen puede ser útil para identificar patrones y posibles causas. Esta información puede ser invaluable para que el médico determine el mejor tratamiento y ayude a los pacientes a controlar su afección eficazmente. Un historial médico completo y, posiblemente, pruebas de alergia pueden proporcionar más información sobre la causa subyacente de la urticaria.
Reconociendo los síntomas de la urticaria
El síntoma distintivo de la urticaria es la aparición de ronchas o habones en la piel que pican y sobresalen. Estas ronchas suelen ser rojas o pálidas, y su tamaño puede variar considerablemente, desde unos pocos milímetros hasta varios centímetros de diámetro. Pueden aparecer en cualquier parte del cuerpo, incluyendo la cara, el tronco, los brazos y las piernas. Las ronchas suelen picar intensamente, causando una gran incomodidad y, a menudo, provocando rascado. Rascarse puede irritar aún más la piel y potencialmente provocar infecciones cutáneas secundarias.
La urticaria puede aparecer repentinamente y desaparecer con la misma rapidez, a menudo durando solo unas horas o incluso minutos. Sin embargo, pueden aparecer nuevas ronchas en otras zonas a medida que las anteriores desaparecen. En algunos casos, la urticaria puede persistir durante días o incluso semanas. La aparición de la urticaria puede ser impredecible, con brotes que aparecen en cualquier momento. La intensidad del picor también puede variar, desde una leve molestia hasta un picor intenso y debilitante que interfiere con el sueño y las actividades diarias.
Además de las ronchas características, la urticaria a veces puede ir acompañada de otros síntomas, según la causa y la gravedad de la afección. El angioedema, una inflamación más profunda que afecta los tejidos subcutáneos, es una posible complicación. Esta inflamación suele afectar la cara, los labios y la garganta, y puede ser especialmente peligrosa si afecta las vías respiratorias, causando dificultad para respirar. Otros síntomas que pueden acompañar a la urticaria incluyen náuseas, vómitos, mareos y dificultad para respirar.
Si experimenta alguno de estos síntomas, especialmente angioedema o dificultad para respirar, es fundamental buscar atención médica inmediata. Estos síntomas pueden indicar una reacción alérgica grave que requiere tratamiento inmediato para prevenir complicaciones potencialmente mortales. El reconocimiento preciso de los síntomas es esencial para un tratamiento médico adecuado y para garantizar la intervención oportuna necesaria para abordar las reacciones graves. El autotratamiento solo debe considerarse en casos leves, y siempre es recomendable consultar a un profesional de la salud para obtener diagnóstico y orientación terapéutica.
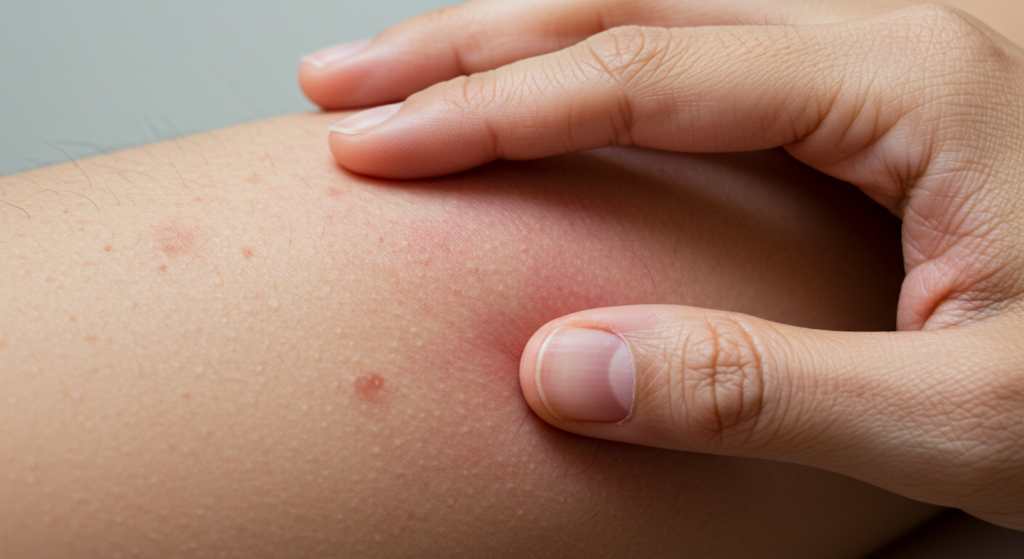
Métodos de tratamiento eficaces para la urticaria
Para casos leves de urticaria, los antihistamínicos de venta libre suelen proporcionar un alivio eficaz. Estos medicamentos, como la difenhidramina (Benadryl) o la cetirizina (Zyrtec), ayudan a bloquear la liberación de histamina, reduciendo la picazón y la inflamación. Aplicar compresas frías en las zonas afectadas también puede ayudar a calmar la picazón y reducir la inflamación. Evitar los desencadenantes conocidos, como ciertos alimentos o medicamentos, es crucial para prevenir futuros brotes. Mantener una buena higiene de la piel también puede ayudar a prevenir infecciones cutáneas secundarias por rascado.
En casos más graves o cuando los tratamientos de venta libre resultan ineficaces, el médico puede recetar antihistamínicos más fuertes u otros medicamentos. Estos pueden incluir antihistamínicos de venta con receta, como fexofenadina (Allegra) o loratadina (Claritin), que pueden ser más eficaces que los de venta libre. Para la urticaria crónica, pueden ser necesarios inhibidores de leucotrienos u otros medicamentos que inhiben el sistema inmunitario. En algunos casos, se pueden utilizar corticosteroides, ya sean orales o tópicos, para reducir la inflamación y controlar los síntomas.
En casos graves, especialmente aquellos acompañados de angioedema o dificultad para respirar, se requiere atención médica inmediata. Se puede administrar epinefrina (adrenalina) para contrarrestar los efectos de una reacción alérgica grave. Puede ser necesaria la hospitalización para monitorear las constantes vitales y brindar la atención de apoyo adecuada. En casos de urticaria crónica, identificar y evitar los desencadenantes es esencial para el tratamiento a largo plazo. Las citas de seguimiento regulares con un médico o alergólogo son importantes para monitorear los síntomas, ajustar el tratamiento según sea necesario y abordar cualquier afección médica subyacente que pueda estar contribuyendo a la urticaria.
Encontrar el enfoque terapéutico adecuado suele implicar un proceso de ensayo y error. Colaborar estrechamente con un profesional de la salud es fundamental para identificar la estrategia de tratamiento más eficaz para las necesidades y circunstancias individuales. Este profesional puede evaluar la gravedad de la urticaria, identificar posibles desencadenantes y recomendar los medicamentos y las estrategias de manejo más adecuados. Una combinación de medicamentos y ajustes en el estilo de vida puede ser necesaria para controlar eficazmente la urticaria crónica y mejorar la calidad de vida. La educación del paciente y el manejo proactivo son cruciales para minimizar el impacto de la urticaria en la vida diaria.

La urticaria, aunque suele ser incómoda, no suele ser una afección potencialmente mortal. Sin embargo, comprender sus causas, reconocer sus síntomas y conocer métodos de tratamiento eficaces es vital para controlar este problema cutáneo común. La atención médica inmediata es crucial en los casos graves, mientras que los casos leves suelen poder controlarse con medicamentos de venta libre y cambios en el estilo de vida. Recuerde consultar con un profesional de la salud para obtener un diagnóstico y recomendaciones de tratamiento personalizadas.
Descubra la experiencia de la Dra. Ebru Okyay, su médico de confianza. dermatólogo en AntalyaYa sea que esté buscando abordar problemas médicos de la piel o mejorar su belleza natural con tratamientos cosméticos, el Dr. Okyay está aquí para ayudarlo. Con atención personalizada y técnicas avanzadas, lograr sus objetivos para la piel nunca ha sido tan fácil.
