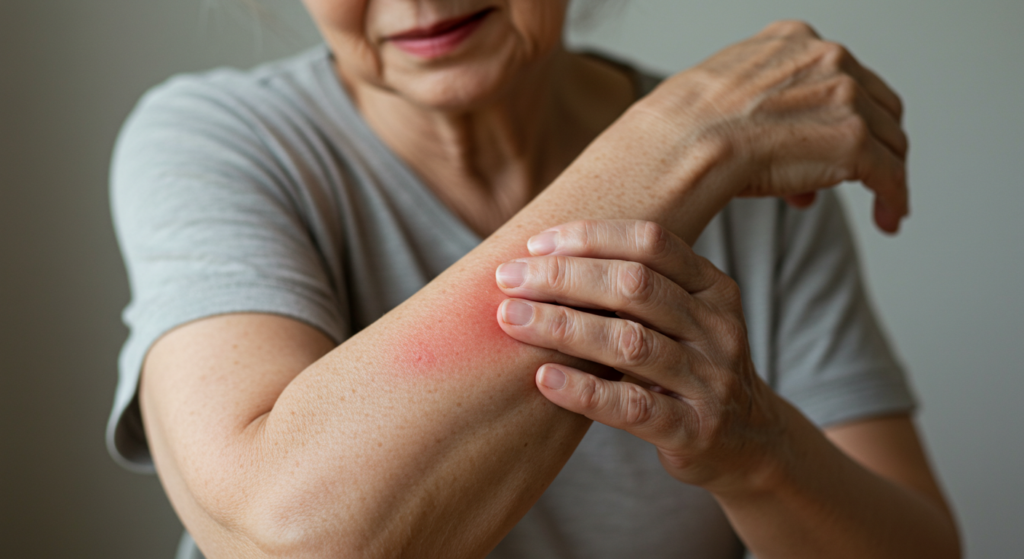
L'eczema, noto anche come dermatite atopica, è una malattia infiammatoria cronica della pelle che colpisce milioni di persone in tutto il mondo. Caratterizzata da1 Prurito, arrossamento, gonfiore e screpolature cutanee: l'eczema può variare da lieve a grave, con un impatto significativo sulla qualità della vita di chi ne soffre. Sebbene i trattamenti topici siano spesso la prima linea di difesa, ci sono casi in cui semplicemente non sono sufficienti. In questi casi, gli operatori sanitari possono prendere in considerazione Farmaci sistemici per gestire la condizione in modo efficace. Questa guida completa approfondirà quando Farmaci sistemici diventare una parte necessaria del trattamento dell'eczema, esplorando i diversi tipi disponibili, i loro benefici, i rischi e ciò che i pazienti dovrebbero sapere.
Comprendere il peso dell'eczema
Prima di discutere Farmaci sistemiciÈ fondamentale comprendere le molteplici sfaccettature dell'eczema. Oltre ai sintomi cutanei visibili, le persone affette da eczema spesso avvertono un prurito intenso che può disturbare il sonno, causare ansia e depressione e interferire con le attività quotidiane. I bambini affetti da eczema possono incontrare difficoltà a scuola e nelle interazioni sociali, mentre gli adulti potrebbero riscontrare ripercussioni sulla loro vita lavorativa e personale. Il ciclo costante di prurito e grattamento può portare a infezioni cutanee, complicando ulteriormente la condizione e richiedendo trattamenti aggiuntivi.
La gravità dell'eczema varia notevolmente da individuo a individuo. Alcuni possono manifestare occasionali lievi riacutizzazioni facilmente gestibili con rimedi da banco e semplici cure per la pelle. Altri, tuttavia, presentano un eczema persistente e grave che interessa ampie zone del corpo, causando un disagio significativo e compromettendo il benessere generale. È in questi casi più gravi che Farmaci sistemici svolgono spesso un ruolo critico.
Il ruolo dei trattamenti topici nella gestione dell'eczema
I trattamenti topici, come i corticosteroidi e gli inibitori della calcineurina, rappresentano il cardine della gestione dell'eczema per molte persone. Questi farmaci vengono applicati direttamente sulla pelle interessata per ridurre l'infiammazione e alleviare il prurito. Anche gli emollienti, o idratanti, sono essenziali per preservare la barriera cutanea e prevenire le riacutizzazioni.
I corticosteroidi topici sono disponibili in diverse potenze, da lievi a molto potenti. La scelta della potenza dipende dalla gravità e dalla localizzazione dell'eczema. Gli inibitori della calcineurina offrono un'alternativa ai corticosteroidi, in particolare per l'uso a lungo termine e su zone sensibili come viso e collo.
Sebbene i trattamenti topici siano efficaci per l'eczema lieve o moderato, potrebbero non essere sufficienti per i soggetti con una malattia grave o diffusa. In queste situazioni, l'infiammazione è spesso troppo estesa per essere adeguatamente controllata con le sole applicazioni topiche. È qui che entra in gioco la necessità di... Farmaci sistemici sorge.
Quando i trattamenti topici risultano insufficienti: riconoscere la necessità di un intervento sistemico
Diversi indicatori suggeriscono che i trattamenti topici potrebbero non essere sufficienti per gestire efficacemente l'eczema, segnalando la potenziale necessità di Farmaci sistemici:
Coinvolgimento esteso della superficie corporea
Quando l'eczema colpisce una grande percentuale della superficie corporea, l'applicazione di farmaci topici può risultare poco pratica e potrebbe non fornire sufficiente sollievo. Farmaci sistemici, d'altro canto, agiscono in tutto il corpo, contrastando l'infiammazione ovunque si manifesti.
Sintomi gravi e persistenti
Se i sintomi dell'eczema, in particolare prurito intenso ed eruzione cutanea diffusa, persistono nonostante l'uso costante e appropriato di trattamenti topici, potrebbe essere necessario un approccio sistemico più efficace. Il prurito incontrollato può influire significativamente sul sonno e sulle attività quotidiane, rendendo necessario un trattamento in grado di fornire un sollievo più ampio.
Frequenti e gravi riacutizzazioni
Gli individui che soffrono di frequenti e gravi riacutizzazioni dell'eczema, che richiedono cicli ripetuti di corticosteroidi topici, possono trarre beneficio da Farmaci sistemici per aiutare a controllare l'infiammazione sottostante e ridurre la frequenza e l'intensità di questi episodi.
Impatto sulla qualità della vita
Quando l'eczema ha un impatto significativo sulla qualità della vita di una persona, influenzando il sonno, l'umore, le interazioni sociali o la capacità di svolgere le attività quotidiane, Farmaci sistemici può essere considerato un modo migliore per controllare i sintomi e migliorare il benessere generale.
Fallimento dei farmaci topici
Se un paziente ha utilizzato diligentemente farmaci topici come prescritto dal proprio medico e non ha riscontrato un miglioramento adeguato nei sintomi dell'eczema, ciò suggerisce un approccio diverso, come Farmaci sistemici, potrebbe essere necessario.
Complicazioni dell'eczema
In alcuni casi, l'eczema grave può dare origine a complicazioni come infezioni cutanee ricorrenti o eczema erpetico (una grave infezione virale). Farmaci sistemici potrebbe essere necessario per controllare l'infiammazione sottostante e prevenire o gestire queste complicazioni.
Introduzione ai farmaci sistemici: un approccio che coinvolge l'intero organismo
Farmaci sistemici Per l'eczema, i farmaci vengono assunti per via orale o iniettiva e agiscono in tutto il corpo riducendo l'infiammazione. Questi farmaci sono in genere riservati a individui con eczema da moderato a grave che non hanno risposto adeguatamente ai trattamenti topici.
Esistono diversi tipi di Farmaci sistemici utilizzati per trattare l'eczema, ognuno con il proprio meccanismo d'azione, benefici e potenziali effetti collaterali. La scelta di Farmaci sistemici dipende da vari fattori, tra cui la gravità dell'eczema, lo stato di salute generale del paziente e la sua risposta ai trattamenti precedenti.
Tipi di farmaci sistemici per l'eczema
Corticosteroidi orali
I corticosteroidi orali, come il prednisone, sono potenti farmaci antinfiammatori che possono fornire un rapido sollievo dalle riacutizzazioni gravi dell'eczema. Agiscono sopprimendo il sistema immunitario, riducendo l'infiammazione in tutto il corpo.
Sebbene altamente efficaci per la gestione a breve termine dell'eczema grave, i corticosteroidi orali sono generalmente sconsigliati per l'uso a lungo termine a causa dei loro potenziali effetti collaterali significativi, tra cui aumento di peso, sbalzi d'umore, aumento del rischio di infezioni, perdita di massa ossea e ipertensione. Pertanto, vengono generalmente utilizzati per brevi cicli di terapia per controllare le riacutizzazioni gravi, spesso come ponte verso altri trattamenti a lungo termine. Farmaci sistemici.
Immunosoppressori tradizionali
Gli immunosoppressori tradizionali agiscono sopprimendo ampiamente il sistema immunitario, riducendo così l'infiammazione associata all'eczema. Questi farmaci sono spesso utilizzati per l'eczema da moderato a grave che non ha risposto ai trattamenti topici. Gli immunosoppressori tradizionali più comuni utilizzati per l'eczema includono:
Ciclosporina
La ciclosporina è un immunosoppressore che agisce inibendo l'attività dei linfociti T, un tipo di cellula immunitaria che svolge un ruolo chiave nell'infiammazione associata all'eczema. Può essere efficace nel controllo dell'eczema grave, ma richiede un attento monitoraggio a causa di potenziali effetti collaterali come problemi renali, ipertensione e aumento del rischio di infezioni.
Metotrexato
Il metotrexato è un altro immunosoppressore talvolta utilizzato per trattare l'eczema grave. Agisce interferendo con la crescita di alcune cellule del corpo, comprese quelle immunitarie. I potenziali effetti collaterali del metotrexato includono problemi al fegato, infiammazione polmonare e soppressione del midollo osseo, che richiedono esami del sangue regolari.
Azatioprina
L'azatioprina è un immunosoppressore che agisce inibendo la produzione di DNA e RNA nelle cellule immunitarie. Può essere efficace nel trattamento dell'eczema, ma possono essere necessarie diverse settimane o mesi per raggiungere il suo pieno effetto. Gli effetti collaterali possono includere nausea, vomito, diarrea e un aumento del rischio di infezioni. Sono necessari esami del sangue regolari per monitorare potenziali problemi al fegato e soppressione del midollo osseo.
Micofenolato Mofetile
Il micofenolato mofetile è un immunosoppressore che agisce inibendo un enzima coinvolto nella produzione di DNA nelle cellule immunitarie. A volte viene utilizzato off-label per il trattamento dell'eczema grave. Gli effetti collaterali comuni includono problemi gastrointestinali come nausea, vomito e diarrea.
Biologici
I farmaci biologici sono una classe più recente di Farmaci sistemici che prendono di mira specifici componenti del sistema immunitario coinvolti nello sviluppo dell'eczema. Questo approccio mirato può portare a minori effetti collaterali diffusi rispetto ai tradizionali immunosoppressori. Diversi farmaci biologici sono stati approvati per il trattamento dell'eczema da moderato a grave:
Dupilumab
Dupilumab è un anticorpo monoclonale che blocca l'azione di due proteine chiave, l'interleuchina-4 (IL-4) e l'interleuchina-13 (IL-13), che sono i principali fattori scatenanti dell'infiammazione di tipo 2 osservata nell'eczema. Viene somministrato tramite iniezione sottocutanea ogni due settimane (o ogni quattro settimane a un dosaggio più elevato). Dupilumab ha dimostrato un'efficacia significativa nel ridurre i sintomi dell'eczema e nel migliorare la qualità della vita, con un profilo di sicurezza generalmente favorevole. Gli effetti collaterali comuni includono reazioni al sito di iniezione e congiuntivite.
Tralokinumab
Il tralokinumab è un altro anticorpo monoclonale che agisce specificamente sull'interleuchina-13 (IL-13). Viene anch'esso somministrato tramite iniezione sottocutanea ogni due settimane. Studi clinici hanno dimostrato che il tralokinumab può migliorare significativamente i sintomi dell'eczema, tra cui la scomparsa della pelle e la riduzione del prurito. Gli effetti collaterali comuni includono infezioni delle vie respiratorie superiori, congiuntivite e reazioni al sito di iniezione.
Lebrikizumab
Lebrikizumab è un anticorpo monoclonale che si lega selettivamente all'interleuchina-13 (IL-13), impedendone il legame al suo recettore e inibendo di conseguenza la segnalazione a valle. Viene somministrato per iniezione sottocutanea ogni due settimane per le prime dosi, seguite da una somministrazione ogni quattro settimane come terapia di mantenimento. Studi clinici hanno dimostrato che lebrikizumab può portare a significativi miglioramenti nei segni e nei sintomi dell'eczema. Gli effetti collaterali comuni includono reazioni al sito di iniezione, congiuntivite e mal di testa.
Inibitori orali della Janus chinasi (JAK)
Gli inibitori JAK orali sono una classe di Farmaci sistemici che agiscono bloccando l'attività delle Janus chinasi (JAK), una famiglia di enzimi che svolgono un ruolo cruciale nelle vie di segnalazione di varie citochine coinvolte nell'infiammazione, comprese quelle implicate nell'eczema. Diversi inibitori delle JAK sono stati approvati per il trattamento dell'eczema da moderato a grave:
Upadacitinib
Upadacitinib è un inibitore selettivo della JAK1, assunto per via orale una volta al giorno. Studi clinici ne hanno dimostrato l'efficacia nel migliorare significativamente la clearance cutanea, ridurre il prurito e migliorare la qualità della vita in adulti e adolescenti con eczema da moderato a grave. Gli effetti collaterali comuni possono includere infezioni delle vie respiratorie superiori, nausea, mal di testa e aumento della creatinina ematica.
Abrocitinib
Abrocitinib è un altro inibitore selettivo della JAK1 somministrato per via orale una volta al giorno. Studi hanno dimostrato che abrocitinib può migliorare rapidamente i segni e i sintomi dell'eczema, incluso il prurito, ed è efficace sia nel trattamento a breve che a lungo termine. Gli effetti collaterali comuni possono includere nausea, mal di testa, infezioni delle vie respiratorie superiori e infezioni da herpes simplex.
Come funzionano i farmaci sistemici per trattare l'eczema
Farmaci sistemici perché agiscono sull'eczema prendendo di mira diversi aspetti del sistema immunitario che contribuiscono all'infiammazione sottostante e alla disfunzione della barriera cutanea caratteristica della condizione.
- Corticosteroidi orali: Riduce l'infiammazione sopprimendo ampiamente il sistema immunitario.
- Immunosoppressori tradizionali (Ciclosporina, Metotrexato, Azatioprina, Micofenolato Mofetile): Sopprimono l'attività di varie cellule immunitarie, come i linfociti T, e interferiscono con la loro funzione.
- Farmaci biologici (Dupilumab, Tralokinumab, Lebrikizumab): Bloccano in modo specifico l'azione delle citochine chiave (IL-4 e/o IL-13) che causano l'infiammazione di tipo 2 nell'eczema.
- Inibitori JAK orali (Upadacitinib, Abrocitinib): Inibiscono l'attività degli enzimi JAK, coinvolti nei percorsi di segnalazione di molteplici citochine pro-infiammatorie.
Modulando queste risposte immunitarie, Farmaci sistemici può ridurre efficacemente l'infiammazione, alleviare il prurito, migliorare la pulizia della pelle e, in definitiva, migliorare la qualità della vita delle persone affette da eczema da moderato a grave.
Benefici dell'uso di farmaci sistemici per l'eczema
Quando i trattamenti topici sono insufficienti, Farmaci sistemici può offrire benefici significativi per le persone affette da eczema:
- Controllo dei sintomi migliorato: Farmaci sistemici può ridurre efficacemente la gravità dei sintomi dell'eczema, tra cui prurito, arrossamento, gonfiore e secchezza della pelle.
- Maggiore pulizia della pelle: Molti Farmaci sistemici, in particolare farmaci biologici e inibitori JAK, possono portare a una significativa schiaritura della pelle, riducendo l'estensione e la gravità dell'eruzione cutanea.
- Riduzione della frequenza e della gravità delle riacutizzazioni: L'uso a lungo termine di alcuni Farmaci sistemici può aiutare a prevenire o ridurre la frequenza e l'intensità delle riacutizzazioni dell'eczema.
- Miglioramento della qualità della vita: Controllando i sintomi dell'eczema, Farmaci sistemici può portare a miglioramenti significativi del sonno, dell'umore, della partecipazione sociale e del benessere generale.
- Potenziale per la gestione a lungo termine: Alcuni Farmaci sistemici, come alcuni immunosoppressori tradizionali, farmaci biologici e inibitori JAK, possono essere utilizzati per la gestione a lungo termine dell'eczema da moderato a grave.
Potenziali rischi ed effetti collaterali dei farmaci sistemici
Mentre Farmaci sistemici Sebbene possano essere molto efficaci, è importante essere consapevoli dei potenziali rischi ed effetti collaterali. Gli effetti collaterali specifici variano a seconda del tipo di farmaco utilizzato.
- Corticosteroidi orali: Gli effetti collaterali a breve termine possono includere sbalzi d'umore, aumento dell'appetito e ritenzione idrica. L'uso a lungo termine può portare a effetti collaterali più gravi come aumento di peso, ipertensione, perdita di massa ossea, diabete e aumento del rischio di infezioni.
- Immunosoppressori tradizionali: La ciclosporina può causare problemi renali e ipertensione. Il metotrexato può avere effetti su fegato e polmoni. L'azatioprina e il micofenolato mofetile possono causare problemi gastrointestinali e aumentare il rischio di infezioni. Il monitoraggio regolare tramite esami del sangue è fondamentale con questi farmaci.
- Biologici: Gli effetti collaterali comuni di farmaci biologici come dupilumab, tralokinumab e lebrikizumab includono spesso reazioni al sito di iniezione e congiuntivite. Sebbene generalmente considerati sicuri, esiste un rischio teorico di infezioni più gravi o reazioni allergiche.
- Inibitori JAK orali: Gli effetti collaterali comuni di upadacitinib e abrocitinib possono includere infezioni delle vie respiratorie superiori, nausea, mal di testa e infezioni da herpes simplex. Possono inoltre verificarsi eventi cardiovascolari più gravi o coaguli di sangue, in particolare nei soggetti con fattori di rischio preesistenti.
È essenziale che i pazienti abbiano una discussione approfondita con il proprio medico sui potenziali rischi e benefici2 di ciascuno Farmaci sistemici prima di iniziare il trattamento. Il monitoraggio e il follow-up regolari sono inoltre fondamentali per gestire eventuali effetti collaterali e garantire l'efficacia del farmaco.
Il processo decisionale: quando i farmaci sistemici sono la scelta giusta?
La decisione di iniziare Farmaci sistemici per l'eczema è una collaborazione tra il paziente e il suo medico, in genere un dermatologoDurante questo processo vengono presi in considerazione diversi fattori:
- Gravità dell'eczema: Farmaci sistemici sono generalmente riservati agli eczemi da moderati a gravi che non hanno risposto adeguatamente ai trattamenti topici.
- Impatto sulla qualità della vita: Se l'eczema influisce in modo significativo sulla vita quotidiana di una persona, nonostante una terapia topica ottimale, Farmaci sistemici può essere presa in considerazione.
- Fallimento dei trattamenti topici: Se un paziente ha utilizzato costantemente farmaci topici come prescritto senza ottenere miglioramenti significativi, potrebbe essere necessario un approccio sistemico.
- Frequenza delle riacutizzazioni: Frequenti e gravi riacutizzazioni che richiedono cicli ripetuti di corticosteroidi topici possono indicare la necessità di un Farmaci sistemici per garantire un migliore controllo a lungo termine.
- Preferenze e stile di vita del paziente: Anche le preferenze del paziente, lo stile di vita e la sua capacità di aderire a un particolare regime terapeutico sono considerazioni importanti. Ad esempio, alcuni pazienti potrebbero preferire i farmaci orali alle iniezioni, o viceversa.
- Stato di salute generale e anamnesi medica: La salute generale del paziente, altre condizioni mediche e eventuali farmaci esistenti saranno presi in considerazione per garantire la scelta Farmaci sistemici è sicuro e appropriato.
- Potenziali rischi e benefici: Una discussione approfondita dei potenziali rischi e benefici di ciascuno Farmaci sistemici L'opzione è essenziale per aiutare il paziente a prendere una decisione informata.
Vivere con l'eczema e i farmaci sistemici
Di partenza Farmaci sistemici per l'eczema può rappresentare un passo significativo nella gestione della condizione. È importante che i pazienti abbiano aspettative realistiche e collaborino a stretto contatto con il loro team sanitario. Ecco alcuni aspetti chiave della convivenza con l'eczema durante il trattamento. Farmaci sistemici:
- Aderenza al trattamento: È fondamentale prendere Farmaci sistemici Esattamente come prescritto dal medico. Saltare le dosi o modificarne il dosaggio senza il consiglio del medico può compromettere l'efficacia del farmaco e potenzialmente causare effetti collaterali.
- Appuntamenti di controllo regolari: Controlli periodici dal dermatologo sono essenziali per monitorare l'efficacia del farmaco, gestire gli eventuali effetti collaterali e apportare le modifiche necessarie al piano terapeutico.3
- Riconoscere e segnalare gli effetti collaterali: I pazienti devono essere consapevoli dei potenziali effetti collaterali del loro Farmaci sistemici e segnalare tempestivamente al proprio medico curante qualsiasi sintomo nuovo o peggioramento.
- Mantenere una buona cura della pelle: Anche mentre sei su Farmaci sistemici, è importante continuare a prendersi cura della pelle in modo adeguato, utilizzando regolarmente prodotti emollienti e pulendola delicatamente per rinforzare la barriera cutanea.
- Gestione dei trigger: Identificare ed evitare i fattori scatenanti noti dell'eczema, come determinati irritanti o allergeni, può aiutare a ridurre la frequenza delle riacutizzazioni.
- Cercare supporto: Vivere con una patologia cronica come l'eczema può essere difficile. Rivolgersi a gruppi di supporto o a professionisti della salute mentale può fornire un prezioso supporto emotivo e pratico.
Il futuro dei trattamenti sistemici per l'eczema
Il campo del trattamento dell'eczema è in continua evoluzione, con la ricerca in corso che porta allo sviluppo di nuovi e innovativi Farmaci sistemiciGli scienziati lavorano costantemente per comprendere meglio i complessi percorsi immunitari coinvolti nell'eczema, aprendo la strada a terapie più mirate ed efficaci con profili di sicurezza migliorati.
I trattamenti emergenti in fase di sviluppo includono ulteriori farmaci biologici mirati a diverse citochine o vie metaboliche, nonché nuovi inibitori di piccole molecole. Questi progressi sono promettenti per offrire più opzioni terapeutiche alle persone con eczema da moderato a grave e migliorare ulteriormente la loro qualità di vita.
Conclusione: i farmaci sistemici come strumento fondamentale nella gestione dell'eczema
Sebbene i trattamenti topici rimangano il fondamento della gestione dell'eczema, Farmaci sistemici svolgono un ruolo cruciale nel controllo della malattia da moderata a grave che non ha risposto adeguatamente a queste terapie. La decisione di utilizzare Farmaci sistemici è un problema significativo che richiede un'attenta valutazione della gravità dell'eczema, del suo impatto sulla qualità della vita, dei potenziali benefici e rischi di ciascun farmaco e delle circostanze individuali del paziente.
Con una gamma di Farmaci sistemici Grazie ai farmaci ora disponibili, tra cui immunosoppressori tradizionali, farmaci biologici e inibitori JAK orali, le persone con eczema grave hanno più opzioni che mai. Questi farmaci possono offrire un sollievo significativo dai sintomi debilitanti, migliorare la pulizia della pelle e il benessere generale.
Se soffri di eczema e ritieni che il tuo attuale piano di trattamento non ti stia offrendo un sollievo sufficiente, è fondamentale discutere le tue opzioni con un dermatologo. Può valutare la tua condizione e determinare se Farmaci sistemici sono adatti a te e ti aiutano a orientarti tra le opzioni disponibili per trovare il trattamento più adatto alle tue esigenze individuali. Ricorda che la gestione efficace dell'eczema è un percorso, e con il giusto piano di trattamento, che include Farmaci sistemici quando necessario, è possibile ottenere miglioramenti significativi nella qualità della vita.
Scopri la competenza della Dott.ssa Ebru Okyay, la tua dottoressa di fiducia dermatologo In Adalia. Che tu voglia risolvere problemi di pelle di natura medica o migliorare la tua bellezza naturale con trattamenti cosmetici, il dott. Okyay è qui per aiutarti. Con cure personalizzate e tecniche avanzate, raggiungere i tuoi obiettivi per la pelle non è mai stato così facile.
