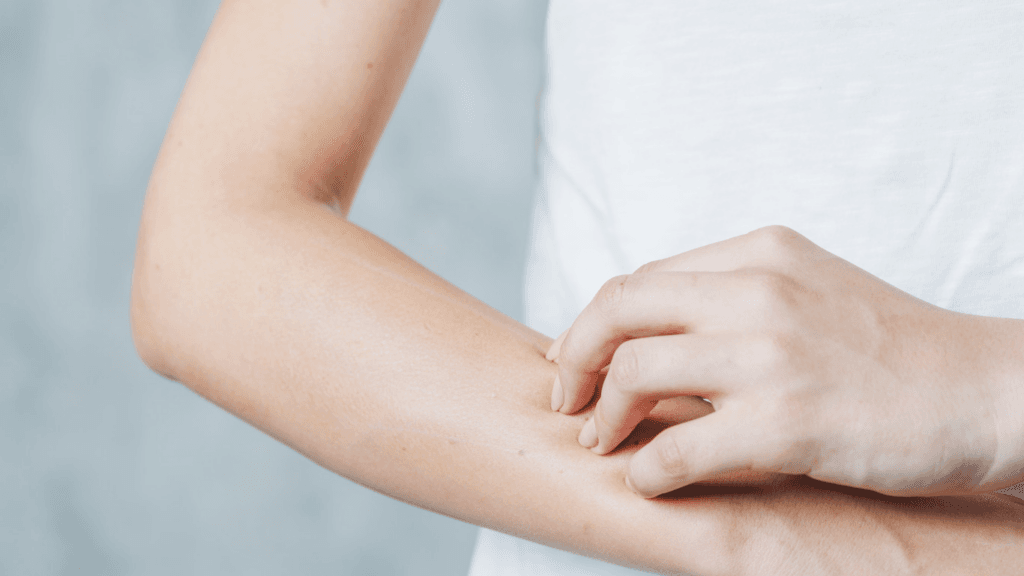
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, often leading to discomfort and social embarrassment. While the exact cause of eczema remains unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may include redness, scaling, blistering, and even secondary infections. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to help manage eczema and improve quality of life.

Eczema: A Skin Condition Overview
Eczema, a chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide, is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. This often leads to discomfort, social embarrassment, and even secondary infections. While the exact cause of eczema remains unknown, it is believed to be a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Symptoms can vary widely, from mild to severe, and may include redness, scaling, blistering, and crusting.
There are several types of eczema, each with its own unique characteristics. Atopic dermatitis is the most common form, often beginning in infancy or early childhood. Contact dermatitis occurs as a result of exposure to irritants or allergens, causing a rash at the site of contact. Dyshidrotic eczema is characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters on the palms, fingers, or soles of the feet. Nummular eczema presents as coin-shaped lesions on the skin, while lichenified eczema is a thickened, leathery patch of skin caused by chronic scratching.
Eczema can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. The constant itch can be debilitating, leading to disrupted sleep, difficulty concentrating, and even depression. In addition, the physical appearance of eczema can be distressing, affecting self-esteem and social interactions.
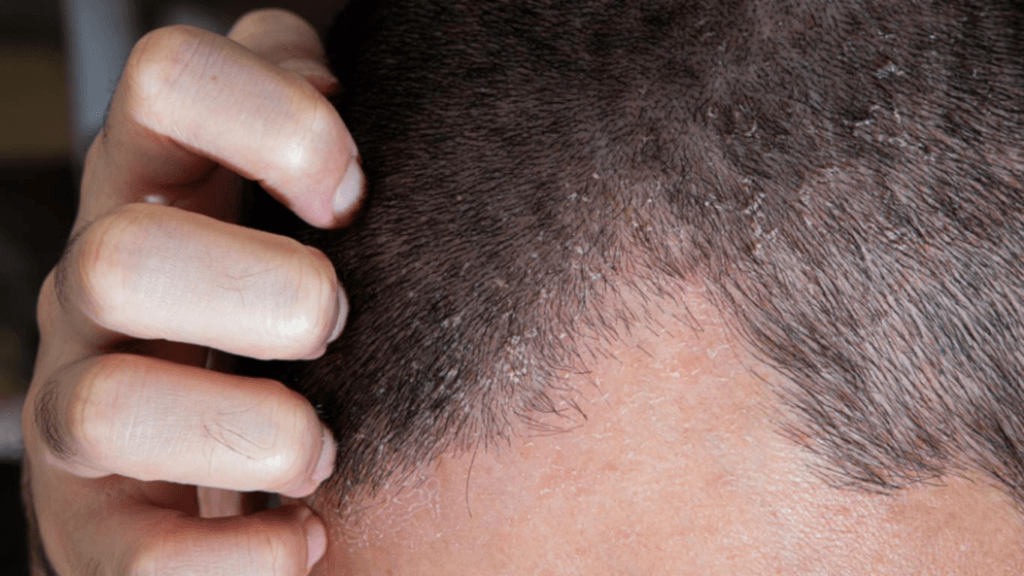
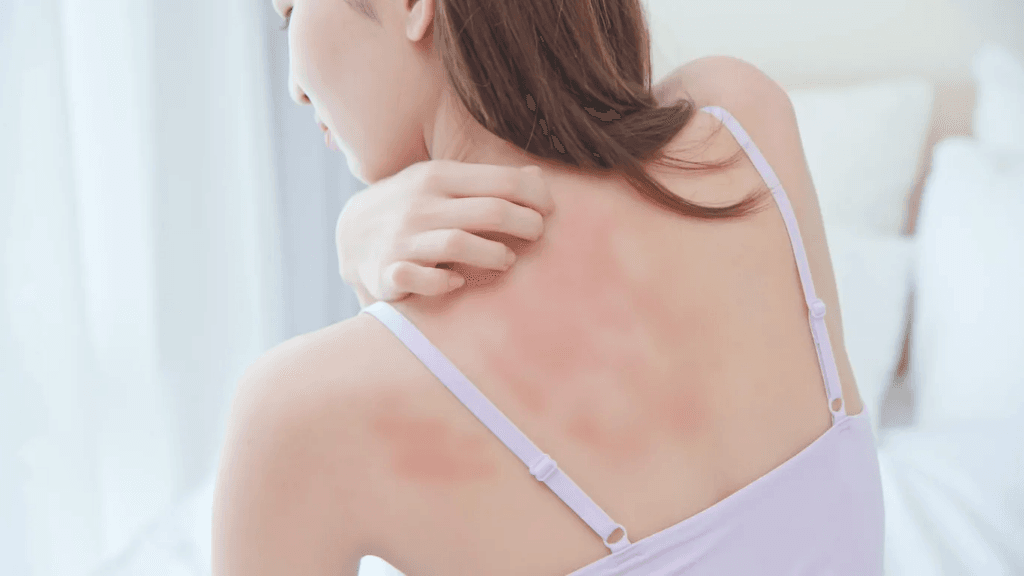
Common Eczema Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs
Eczema can manifest in various ways, but certain symptoms are commonly observed. The most prominent symptom is intense itching, which can be so severe that it disrupts sleep, work, and daily activities. The affected skin may appear dry, scaly, and rough, often resembling sandpaper. In more severe cases, the skin may become red, swollen, and cracked, increasing the risk of infection.
Other common symptoms include blistering, crusting, and oozing. These can occur when the skin becomes irritated or damaged due to scratching or exposure to allergens. Eczema can also lead to thickening of the skin, known as lichenification, which can be difficult to treat.
The location of eczema symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. In infants, eczema often appears on the face, scalp, and diaper area. As children grow older, the affected areas may shift to the folds of the elbows, knees, and wrists. Adults may experience eczema on their hands, feet, neck, or upper body.
It is important to note that the severity of eczema symptoms can fluctuate over time. Periods of remission, when symptoms are mild or absent, may be followed by flare-ups, when symptoms worsen. Identifying and avoiding triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Eczema Treatment Options: Finding Relief
While there is no cure for eczema, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The most appropriate treatment approach will depend on the severity of the condition, the patient’s age, and the underlying cause.
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate eczema. These include moisturizers, corticosteroids, and topical calcineurin inhibitors. Moisturizers help to hydrate the skin and reduce itching, while corticosteroids and topical calcineurin inhibitors can help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
For more severe cases of eczema, systemic treatments may be necessary. These include oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics. Oral corticosteroids can provide rapid relief from symptoms but should be used with caution due to potential side effects. Immunosuppressants and biologics are newer treatment options that can be effective for severe or resistant cases of eczema.
Light therapy is another option for managing eczema. This involves exposing the affected skin to ultraviolet (UV) light, which can help reduce inflammation and control itching. There are two types of light therapy: narrowband UVB and excimer laser.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can also play a role in managing eczema. Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as allergens or irritants, can help prevent flare-ups. Keeping the skin hydrated with regular moisturizing is essential, and avoiding harsh soaps and detergents can help minimize irritation. Stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises or meditation, can also be beneficial for individuals with eczema.
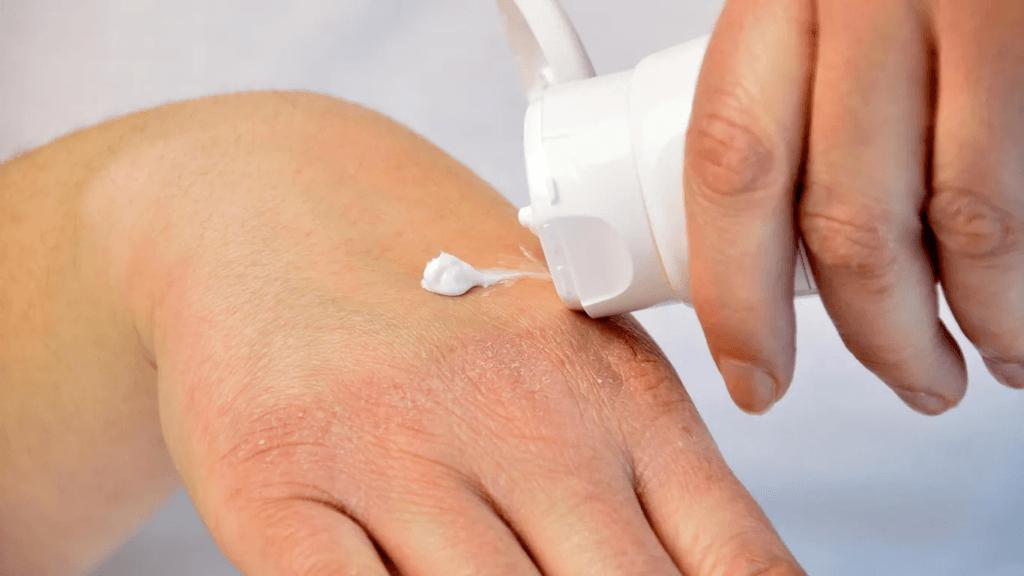
Skincare Tips for Eczema: Nourishing and Protecting
Proper skincare is essential for managing eczema and preventing flare-ups. Here are some tips to help keep your skin healthy and hydrated:
- Moisturize regularly: Apply a fragrance-free moisturizer to damp skin immediately after bathing or showering. This helps to lock in moisture and prevent dryness.
- Choose gentle products: Avoid harsh soaps, detergents, and fragrances that can irritate the skin. Opt for gentle, hypoallergenic products instead.
- Avoid irritants: Identify and avoid triggers that can exacerbate eczema symptoms. These may include allergens, irritants, or harsh fabrics.
- Take lukewarm baths: Hot water can dry out the skin, so opt for lukewarm baths or showers. Limit bathing time to 10-15 minutes.
- Pat dry gently: After bathing, pat your skin dry with a soft towel instead of rubbing. Rubbing can irritate the skin and worsen eczema symptoms.
- Use cotton clothing: Wear soft, loose-fitting clothing made from breathable fabrics like cotton. Avoid fabrics that can irritate the skin, such as wool or polyester.
- Protect from the sun: Exposure to sunlight can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Wear protective clothing and sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of 30 or higher when spending time outdoors.
- Manage stress: Stress can trigger or worsen eczema flare-ups. Practice stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
By following these skincare tips and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage eczema and improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, often leading to discomfort and social embarrassment. While the exact cause remains unknown, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to contribute to its development.
Several treatment options are available to manage eczema and improve quality of life. These include topical treatments, systemic treatments, light therapy, and lifestyle modifications. By working closely with a healthcare provider and implementing appropriate strategies, individuals with eczema can effectively control symptoms and enjoy a better quality of life.
If you are struggling with eczema, it is important to seek professional help. A dermatologist can diagnose the condition, recommend appropriate treatments, and provide guidance on managing symptoms. By taking proactive steps to care for your skin and address the underlying causes of eczema, you can reduce the impact of this condition on your daily life.
Discover the expertise of Dr. Ebru Okyay, your trusted dermatologist in Antalya. Whether you’re looking to address medical skin concerns or enhance your natural beauty with cosmetic treatments, Dr. Okyay is here to help. With personalized care and advanced techniques, achieving your skin goals has never been easier.
