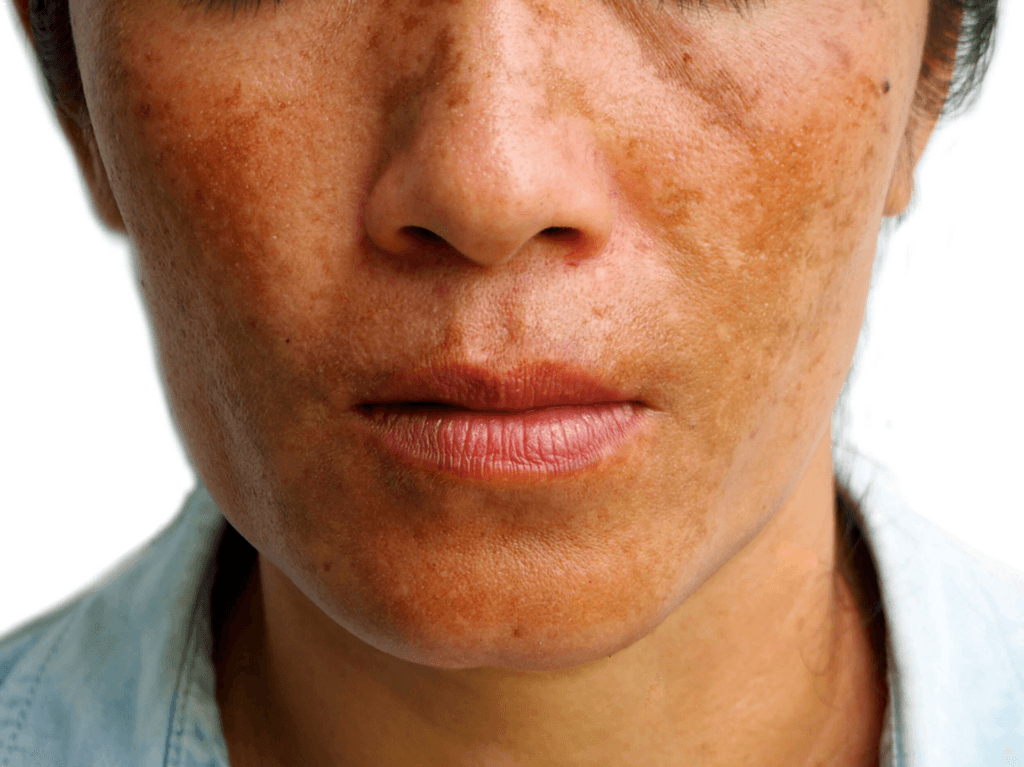
Melasma, a common skin condition, is characterized by dark, discolored patches on the face. While the exact cause of melasma is unknown, research suggests that vitamin D deficiency may play a role in its development. This article explores the relationship between vitamin D and melasma, discussing the causes and symptoms of melasma, the potential link to vitamin D deficiency, and treatment options for managing the condition.
Vitamin D and Melasma: An Overview
Vitamin D is a nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including calcium absorption and bone health. Recent studies have suggested that vitamin D may also influence skin health, including pigmentation. Melasma is a condition that causes hyperpigmentation, or darkening of the skin, in specific areas of the face, such as the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip.
Melasma: Causes and Symptoms
Melasma is a complex condition with multiple potential causes. Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or with the use of hormonal contraceptives, are common triggers. Sun exposure, genetics, and certain medications can also contribute to the development of melasma. The primary symptom of melasma is the appearance of dark, irregular patches on the face, which can range in color from light brown to dark gray. These patches are often symmetrical and can vary in size and shape.
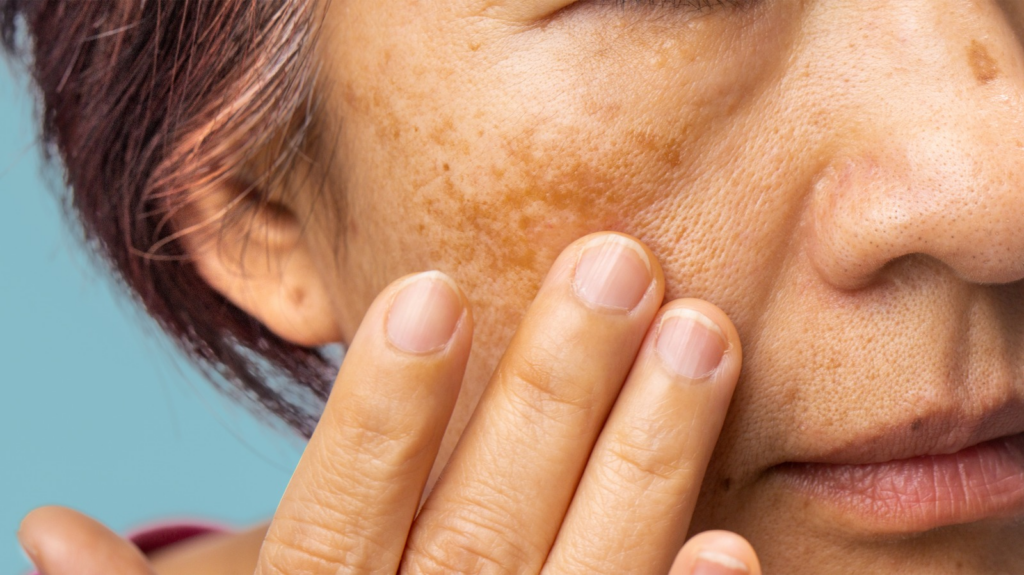

Vitamin D Deficiency and Melasma
Research has shown a potential link between vitamin D deficiency and melasma. Vitamin D is known to regulate the production of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. In individuals with vitamin D deficiency, melanin production may be disrupted, leading to hyperpigmentation and the development of melasma. Studies have found that people with melasma have lower levels of vitamin D in their blood compared to those without the condition.
Treatment Options and Prevention
Treatment for melasma typically involves a combination of topical medications, such as hydroquinone or azelaic acid, and sun protection. Topical retinoids, which are derived from vitamin A, may also be used to reduce hyperpigmentation. In some cases, oral medications, such as tranexamic acid, can be prescribed to inhibit melanin production. Preventing melasma involves limiting sun exposure, using sunscreen, and avoiding hormonal triggers whenever possible. Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels through diet and supplementation may also be beneficial in reducing the risk of developing melasma.
While further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between vitamin D and melasma, evidence suggests that vitamin D deficiency may be a contributing factor in the development of this condition. By maintaining adequate vitamin D levels, individuals may be able to reduce their risk of developing melasma or improve the effectiveness of their treatment. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements or making significant changes to your diet or skincare routine.
Discover the expertise of Dr. Ebru Okyay, your trusted dermatologist in Antalya. Whether you’re looking to address medical skin concerns or enhance your natural beauty with cosmetic treatments, Dr. Okyay is here to help. With personalized care and advanced techniques, achieving your skin goals has never been easier.
FAQ
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes dark, discolored patches, often on the face. These patches can vary in color from light brown to dark gray.
What Causes Melasma?
While the exact cause of melasma is unknown, several factors can contribute to its development:
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, birth control pills, and hormone replacement therapy can trigger melasma.
- Sun Exposure: Excessive sun exposure can worsen melasma.
- Genetics: A family history of melasma may increase your risk.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can contribute to melasma.
How is Melasma Linked to Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin color. Research suggests that vitamin D deficiency may disrupt melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation and the development of melasma.
What are the Treatment Options for Melasma?
Several treatment options are available for melasma:
- Topical Treatments: Creams containing hydroquinone, tretinoin, or azelaic acid can help lighten the discolored patches.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels can exfoliate the skin and improve pigmentation.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target the pigmented areas and reduce their appearance.
- Sun Protection: Using sunscreen with a high SPF can help prevent melasma from worsening.
Can Vitamin D Supplements Help with Melasma?
While vitamin D supplements may be beneficial for overall health, their direct impact on melasma is still being studied. It’s essential to consult with a dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment.
How Can I Prevent Melasma?
To prevent melasma, consider the following tips:
- Limit Sun Exposure: Avoid excessive sun exposure, especially between 10 AM and 4 PM.
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Cover up with hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves to protect your skin.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If you have concerns about melasma, seek professional advice.
